CO2 is one of the most important inputs in turfgrass. The turf critically needs to separate the carbon from oxygen and convert the carbon into a carbohydrate using water and solar radiation (Photosynthesis).
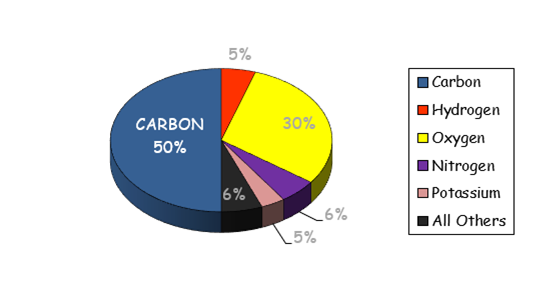
CARBON makes up 50% of the turf.
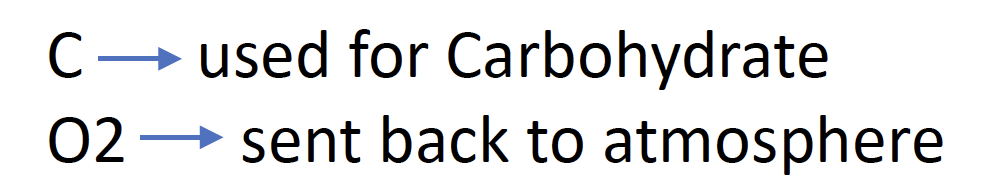
When the plant does not have enough CO2 to convert to carbohydrates, the plant’s rubisco uses O2 instead which can create free radicals, damaging plant cells. Turf Managers can create more CO2 in the ground by using calcium carbonate (CaCO3) and Floratine’s CalpHlex soil product. Then, more CO2 coming out of the soil can be captured by the plant’s stomates, located on the underside of the leaf blades.
Balancing Metabolic Equilibrium
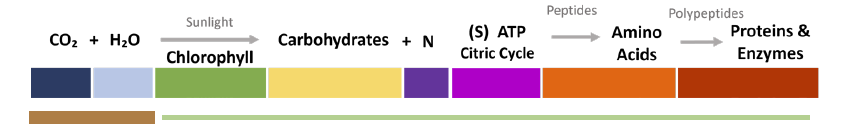
When the plant captures more CO2, it can create more downstream Proteins and Enzymes, making a stronger and healthier plant.
HOW IT WORKS

CALPHLEX promotes conversion of insoluble calcium to soluble form and releases CO3.
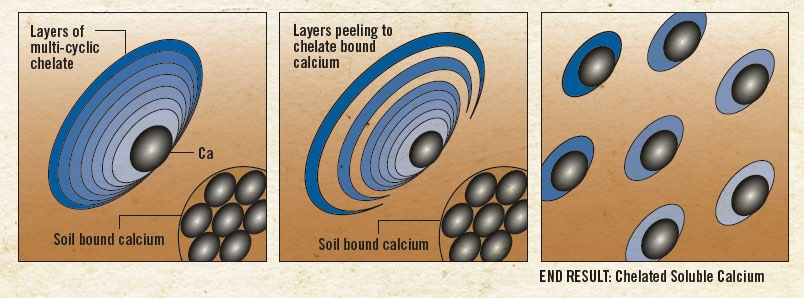
As CalpHlex liberates the Ca from the CO3, it then chelates the calcium, preventing rebinding with the carbonate or any other anions and keeping the calcium in a plant available soluble form.
The soil microbes then take one oxygen from the CO3 leaving it as CO2.
CalpHlex should be used when calcium levels in the soil are above 500 ppm.
IF SOIL CALCIUM IS BELOW 500 PPM, THEN ADD 98G

CalpHlex works best when used with a high cal lime source like Calcium Products 98G limestone. No need to worry about raising soil pH because 98G only has a pH level of 7.6. A 10-pound rate (per 1,000 sq.ft.) will only raise pH by 0.1 point, while adding 150-200 ppm of calcium to the soil.
For example, if soil pH is 6.4, then it could raise to 6.5 pH and if soil calcium is 400 ppm, then it will raise to 550-600 ppm.
